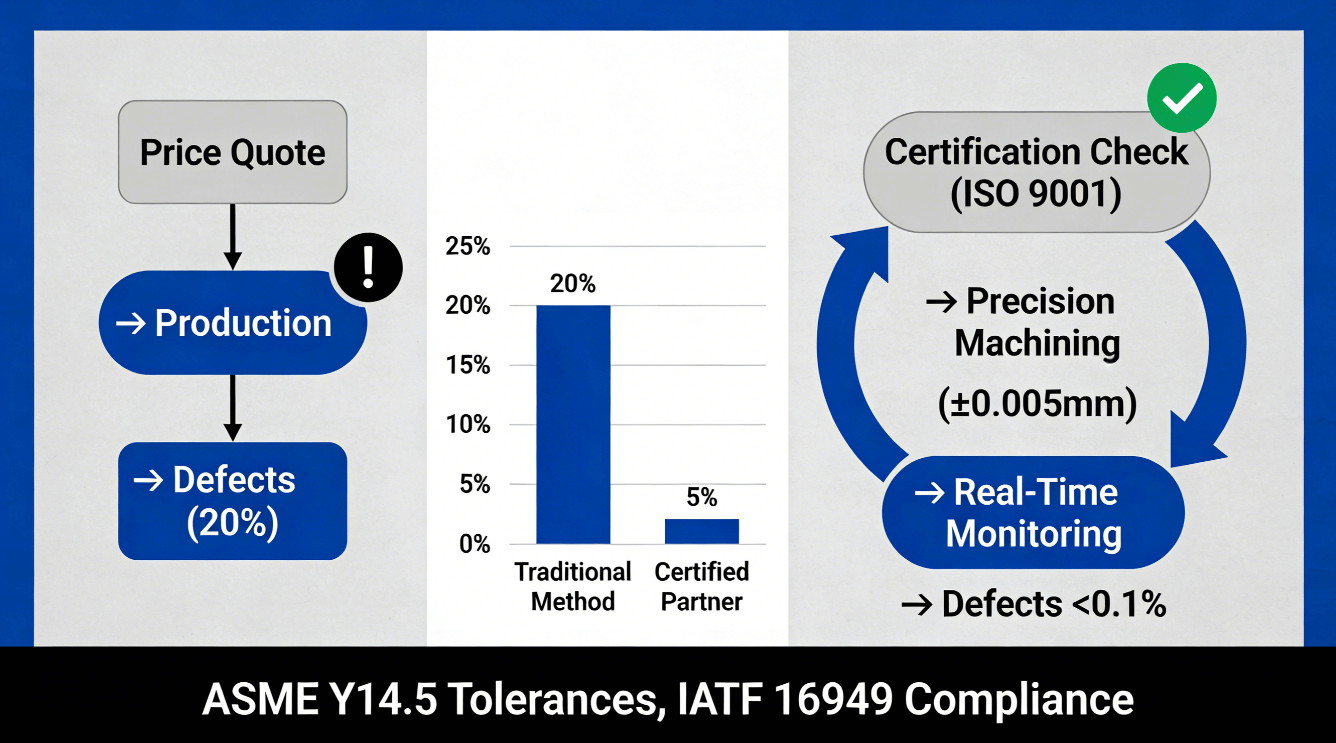
For all custom part projects in the modern competitive manufacturing world, the selection of the wrong CNC turning supplier is a critical problem. According to industry trends, such as those reported by McKinsey for global manufacturing, as many as 40% of these projects still go through extraordinary cost overruns, significant delays in delivery, and unacceptable defect rates due to inappropriate partner selection. In addition, this often arises from a conventional selection process that relies on initial price quotes instead of an expansive technical competency, certification, and sustainable production system evaluation. Businesses are consequently very vulnerable to huge quality and financial risks.
The article presents a structured approach, based on international standards such as ISO 9001, to enable the manufacturing engineer to carefully evaluate and choose a CNC turning partner. This will ensure accuracy, compliance, and cost efficiency over the long term, actually meeting the core challenges of production today.
What Are the Critical Certifications to Verify When Choosing a CNC Turning Partner?
Selecting a business partner based only on machinery is a ready trap to fall into. Checking off important certifications is the first and most important element for de-risking in a supply chain. These certifications mean a great deal more than being a trophy on a wall because they represent a system scalable for consistency and quality.
1. The Role of ISO 9001 in Basic Quality Management
ISO 9001 ensures that there is satisfaction of minimum requirements for a quality management system being in place. The supplier being ISO 9001 certified ensures it adheres to continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and management of its processes as well. ISO 9001 is the name defined by the International Organization for Standardization as a method that ensures it satisfies “customers and legal requirements,” which is essential in any manufacturing venture. ISO 9001 is at this time considered the recognized quality management system globally.
2. Industry-Specific Regulations: IATF 16949 and AS9100D
In highly reliable industries, it’s not sufficient to simply have certification. In the auto sector, for example, it’s necessary to have IATF 16949 certification, which extends ISO 9001 in terms of strict requirements for failure prevention and minimal waste. In a similar vein, to do business in aerospace industries, it’s necessary to have AS9100D certification, for which strong configuration management and traceability are key concerns. Suppliers with AS9100D certification can provide reliable online custom CNC turning services, ensuring aerospace-grade precision.
3. Ensuring Compliance and Traceability
The real benefit here is in the ability they offer in enforcing processes and traceability. Each phase, right from inspection in the raw materials all the way until shipment, is documented. This goes beyond paperwork as it allows for root cause analysis in case there’s a problem, eliminating the same in the future. A company that has an advanced QMS will be able to identify and correct any issue in your project in no time.
What is the Role of Precision Tolerance in Custom CNC Turning Part Success?
Tolerances are the language of design intent. The need to specify and maintain close tolerances, in some cases as low as ±0.005mm, is not negotiable if components are expected to fit, function, and perform in assemblies. The cost of failure is catastrophic.
1. Understanding Design Intent via ASME Y14.5
The ASME Y14.5 standard is the recognized guide for application in Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T). This standard establishes a universal language in describing the definition of tolerances in any engineering drawing. An effective CNC turning outsourcing collaborator has to know how to interpret these symbols correctly for the successful creation of parts as per the designer’s intention. The standard removes any possible ambiguity in understanding the drawing, as interpreted by the designer and the manufacturer, and plays a vital role in ensuring functional compatibility.
2. Relationship between Tolerance Control and Assembly Failure Rates
Data proves that well-managed precision tolerances can cut down assembly failure rates by up to 25%. As an example, one medical device project experienced compatibility issues due to loosely controlled tolerances. This resulted in iterative redesigns. However, a partner with leading metrology equipment, like CMMs, will be able to validate dimensions against the CAD model to ensure the part is right the first time. This provides a huge reduction in the development cycle.
3. Advanced Metrology for Verification
Holding a tolerance is one thing; proving it is another. Beyond basic calipers, advanced measuring tools such as CMMs and optical comparators, enable proving complex geometries and tight tolerances. First-article inspection capability and reports are key indicators of inspection and an overall quality culture from a supplier. This data-driven approach replaces guesswork with certainty.
What cost factors should be considered other than the initial quote in CNC Turning?
The most costly mistake an engineer can make is focusing only on the initial unit price. A holistic approach in evaluating the Total Cost of Ownership brings to light some other hidden expenses that will affect the profitability of the project for the long term.
- Unearthing Hidden Costs: Rework, Logistics, and Compliance: The real cost of a part considers rework, delay, and compliance fines. For instance, a part that shows up at your facility and fails quality checks incurs not just the part cost, but shipping, delayed production, and expedited fees for its replacement. In addition, regulations from bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency note that sustainable manufacturing can offer cost benefits in terms of reduced waste streams, which can also save material costs.
- The Total Cost of Ownership Model: A sturdy TCO model should also consider material utilisation rates, longevity of tooling, and administrative overhead. An electronics company, upon employing this model, felt that a slightly higher-priced but efficient partner actually saved them $100,000 annually by minimizing disruptions and maximizing yield. The shift in perspective is important to make informed choices about selecting a supplier.
- Strategic Partnerships over Transactional Buying: Viewing a CNC turning supplier not as a vendor, but rather as a strategic partner, uncovers more value. A partner who is invested in your success will provide early Design for Manufacturability (DFM) advice to propose mods that simplify machining, reduce costs, and enhance performance without sacrificing function. This collaborative approach minimizes costly changes down the line.
Advanced technology, such as AI and IoT, improves CNC turning services.
Industry 4.0 is reengineering machine shops into smart, connected operations. The use of Industry 4.0 technologies is no longer a nicety-to-have but an absolute must for peak performance, predictability, and cost control.
1. AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance for Minimal Downtime
Through IoT sensors, AI algorithms track and keep updated on the spindle’s load, temperature, and vibrations in real time. The data thus collected can then be used to enable predictive maintenance scheduling of a function just before a likely failure, rather than depending on a fixed calendar basis. As noted in the analyses of manufacturing innovation, this approach can reduce unplanned machine downtime as much as 30%, which assures your projects remain on schedule.
2. IoT and Real-Time Process Monitoring
Sensors imbedded in the machine ensure there is a constant feedback process in place. They can identify the faintest signals of either wear in the tools or cutting forces, which can be corrected automatically or through notifications to the person operating the machine. This is achieved while maintaining constant quality and ensuring Overall Equipment Effectiveness of 90% or higher, which is considerably different from the usual approach.
3. Data-Driven Optimization and Digital Twins
Suppliers are able to integrate machine data to create a manufacturing execution system (MES). This makes possible the simulation of toolpaths before any metal is machined to create a twin of the machining process. This saves energy and makes the workflow more efficient. For more information on how these innovations are used in the industry, refer to the insights in expert CNC turning services blogs.
What Role Does Material Selection Play in Achieving Durability for Custom Parts?
This is what will immediately affect the part’s performance and price. This is where the inexperienced supplier may not know what to do, and it would fail prematurely. The experienced supplier is the consultant regarding the selection of the material.
- Balancing Performance Properties and Cost: For examples such as titanium alloys or aluminum alloys, it is necessary to make compromises in relation to strength to weight ratio, corrosion resistance, or cost considerations. Information derived from sources such as The ASM Handbook is very important for data related to fatigue strength and material properties. An aerospace part, for example, will necessitate using titanium for its strength in heavy environmental situations, while an electronic case will call for aluminum due to its conductive properties.
- The Critical Link to Design For Manufacturability (DFM): Materials selection cannot be dissociated from DFM. The machinability index of a material affects machinability-related factors such as machining time and cost. With knowledge of a complete material database, a component supplier can assist a designer in identifying other materials that have the desired performance but are easier to machine and less prone to defects due to machinability problems.
- Long-Term Reliability and Compliance: In regulated markets, it’s not only about performance properties but also about compliance with regulations. Materials should come with a mill test report that certifies their contents and properties. An experienced supplier should know all this and get his materials from reliable sources to ensure that the final product meets all the requirements based on that product’s service conditions.
How to Assess a Supplier’s Quality Control System for Zero-Defect Manufacturing?
A contemporary quality control system will be proactive, data-driven, and integrated in the manufacturing process. This will be the last defense in ensuring zero-defect manufacturing and that all parts meet all specifications.
1. Statistical Process Control (SPC) for Proactive Management
Apart from final inspection, an intelligent quality control process has to incorporate Statistical Process Control (SPC) methodology. Data collection on a continuous basis during the production phase is required in this process to detect process stability. The key characteristics of any product are plotted on control charts to reveal trends towards specification limits to take corrective actions before producing any non-conforming units.
2. The Importance of First-Article and In-Process Inspections
The first article inspection ensures the entire product is validated before full start-up of production. Further inspections at intervals ensure conformity is being adhered to. The first article inspection is stringent in medical devices based on ISO 13485 regulations, focusing on risk management and traceability in medical devices. The supplier using automated systems for inspection is able to guarantee defect rates at Parts Per Million levels as low as 50, as against the industry standard of 500 and above.
3. Comprehensive Documentation and Continuous Improvement
The end product of an efficient QC process is not only good product but also supporting documentation. There is objective proof of compliance with detailed inspection reports. The data from non-conformances is also used in this process for continuous improvement, whereby data from any non-conformances is subject to analysis for root causes of such incidents to make permanent corrections to prevent future repeating and to continually improve on quality.
Conclusion
As a manufacturing engineer embarks on the journey of selecting a CNC turning supplier, it is important for them to shift focus away from mere comparisons. A comprehensive assessment including a thorough grasp of important certifications, precision tolerancing knowledge, a precise perspective on total costs, utilization of latest technologies, material choices, and a sound quality control process can help a manufacturing engineer in their decision-making process. This will also enable the manufacturing engineer to steer away from expensive mistakes while cutting down errors by at least 30%. The ISO 9001 and ASME Y14.5 standards provide a sound basis for such a comprehensive approach.
FAQs
Q1: What is the normal lead time for custom-made CNC turned parts?
A: The lead time will depend on complexity; however, having an efficient collaboration partner can help facilitate prototyping in 3-5 days and 2-3 weeks for production. The timeline will depend on different requirements, such as material use and validation of designs, for which the timeline will be decided. Efficient suppliers will have access to digital twin technology to allow functionality for ISO 9001.
Q2: In what way is CNC turning different from CNC milling in the case of complicated shapes?
A: Turning involves rotating the work material against a fixed cutting tool best suited for producing cylindrical shapes such as shafts. Milling involves moving a cutting tool in a rotating manner about a fixed work material. Turning is best for mass production of rotatable symmetric objects. Milling can produce geometrically complex objects. Choose according to the geometry of the object as per ASME Y14.5.
Q3: What are some cost-efficient materials for producing high-volume turned components using CNC turning?
A: Cost-effective materials like Aluminum and Stainless Steel have a balance of costs and performance for productions above 10,000 units by cutting part costs by 20-30% through optimal machining parameter usage. Yet, their usage should adapt to their applications depending upon their strengths, for example, higher usage of titanium for aerospace applications.
Q4: Are tight tolerance values under ±0.01 mm possible in CNC turning?
A: Yes, high suppliers have the tolerance of +-0.005mm, which is done through precision lathes and CMMs. This needs to be calibrated in strict adherence to the guidelines of the standard IATF 16949. This will not cause any problems of assembly in the healthcare industry.
Q5: Ways to cut cost without reducing quality in CNC turning.
A: Use DFM principles to reduce material usage and tool pathing. Consider bulk orders with standardized specs to realize a possible 15% reduction in expense. Process automation helps lower labor costs. Just ensure AS9100D certification isn’t compromised when going for the lowest price.
Author Bio
The writer is a precision manufacturing specialist at LS Manufacturing, a company that helps engineers and researchers overcome difficult part designs in aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors. The company has the required certifications for delivering quality services, as they utilize advanced technologies. For more information, contact them today for a free, no-obligation project evaluation and DFM analysis.











